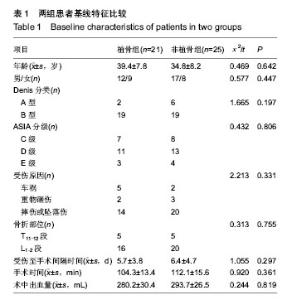
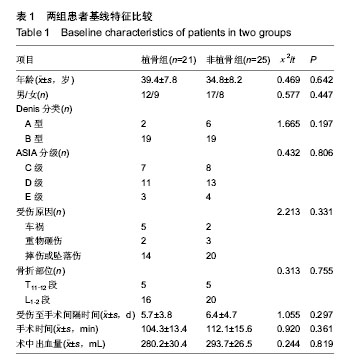
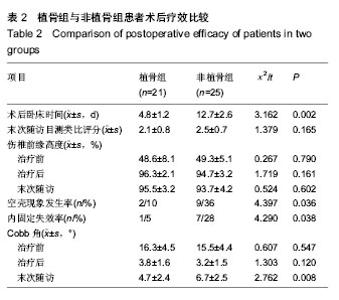
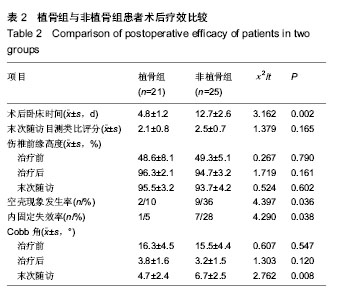
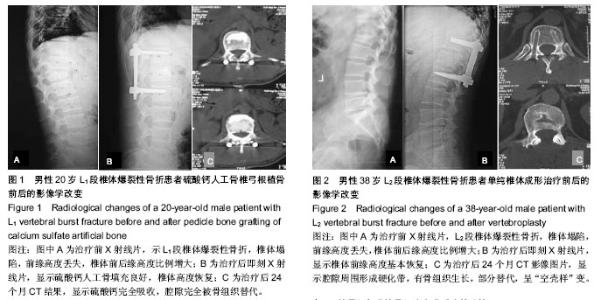
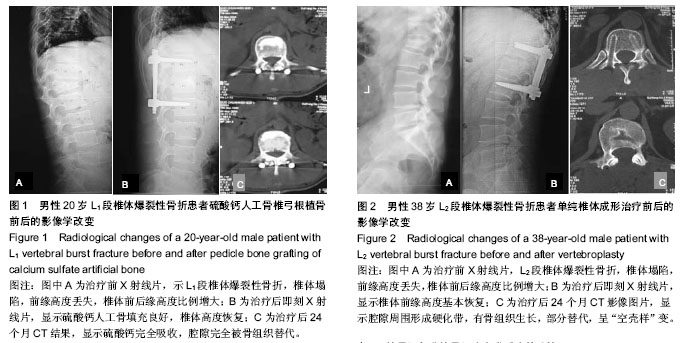
| [1] 曾至立,程黎明,高生,等. 短节段椎弓根螺钉固定结合椎体增强术治疗胸腰椎爆裂性骨折[J].中华骨科杂志,2011,31(9): 927-931.
[2] Korovessis P,Hadjipavlou A,Repantis T.Minimal invasive short posterior instrumentation plus balloon kyphoplasty with calcium phosphate for burst and severe compression lumbar fractures.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2008;33(6):658-667.
[3] 胡海刚,谭伦,林旭,等.经伤椎椎弓根植骨置钉后路复位内固定术治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011,21(8):663-668.
[4] 方涛林,李熙雷,董健,等.前路小切口手术椎体切除 MACS-TL 治疗胸腰椎脊柱转移性肿瘤[J].临床肿瘤学杂志,2010,15(5): 409-413.
[5] 崔文岗,石岩,肖德明.硫酸钙人工骨修复骨缺损的应用研究进展[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2013,10(5):21-23.
[6] 占蓓蕾,叶舟.经椎弓根撬拨复位与椎体成形治疗胸腰椎爆裂性骨折[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2011,5(2):169-171.
[7] Dreesmann H.Ueber knochenplombierung.Beitr Klin Chir. 1892;9:804-810.
[8] Peltier LF.The use of plaster of Paris to fill defects in bone. J Clin Orthop. 1961;(21):1-31.
[9] Mirzayan R,Panossian V,Avedian R,et al.The use of calcium sulfate in the treatment of begnin bone lesions.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2001;83-A(3):355-358.
[10] Alexander DI,Manson NA,Mitchell MJ.Efficacy of calcium sulfate plus decompression bone in lumbar and lumbosacral spinal fusion: preliminary results in 40 patients.Cana J Surg. 2001;44(4):262.
[11] Urban RM,Turner TM, Hall DJ, et al. Healing of large defects treated with calcium sulfate pellets containing demineralized bone matrix particles. Orthopedics.2003; 26(5 Suppl): s581-5.
[12] 张闻力,刘浩,李坛珠,等.医用硫酸钙人工骨在脊柱结核手术中的应用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2007,15(9):652-655.
[13] 罗一,邓展生,贺达仁.胸腰段爆裂性骨折的手术策略选择[J].医学与哲学:临床决策论坛版,2011,32(6):28-29.
[14] 赵正琦,顾振芳,孙先泽.经椎弓根植骨椎体成形内固定治疗胸腰椎爆裂骨折[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2010,24(9):1143-1144.
[15] 杨飞,武永刚.经椎弓根植骨椎体成形结合椎弓根钉固定治疗胸腰椎骨折远期疗效观察[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2009,17(12): 887-890.
[16] 崔勇,孟庆刚,王鹏,等.注射型磷酸钙人工骨椎体后凸成形固化治疗骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩骨折[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(34):6440-6444.
[17] 郑先雨,何家才.医用硫酸钙OsteoSet修复颌骨缺损的疗效评价[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2012,26(1):87-90.
[18] Liao JC, Fan KF,Keorochana G,et al.Transpedicular grafting after short-segment pedicle instrumentation for thoracolumbar burst fracture: calcium sulfate cement versus autogenous iliac bone graft.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2010;35(15):1482-1488.
[19] Crawford RJ, Askin GN. Fixation of thoracolumbar fractures with the Dick fixator: the influence of transpedicular bone grafting.Eur Spine J.1994;3(1):45-51.
[20] Leferink V,Zimmerman K,Veldhuis E,et al.Thoracolumbar spinal fractures: radiological results of transpedicular fixation combined with transpedicular cancellous bone graft and posterior fusion in 183 patients. Eur Spine J.2001;10 (6): 517-523.
[21] Ma YQ,Li XL,Dong J.Is it useful to apply transpedicular intracorporeal bone grafting to unstable thoracolumbar fractures? A systematic review.Acta Neurochirurgica. 2012; 154(12):2205-2213.
[22] Wang JG,Wu H,Ding XL,et al.Treatment of thoracolumbar vertebrate fracture by transpedicular morselized bone grafting in vertebrae for spinal fusion and pedicle screw fixation.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci.2008;28(3):322-326.
[23] Walsh WR,Morberg P,Yu Y,et al.Response of a calcium sulfate bone graft substitute in a confined cancellous defect.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2003;(406):228-236.
[24] Stubbs D,Deakin M,Chapman-Sheath P,et al.In vivo evaluation of resorbable bone graft substitutes in a rabbit tibial defect model.Biomaterials.2004;25(20):5037-5044.
[25] 张贵林,荣国威.脊柱胸腰段骨折术后椎弓根螺钉断裂及弯曲松动的原因分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2000,20(8):470-472.
[26] Scarano A, Orsini G, Pecora G, et al. Peri-implant bone regeneration with calcium sulfate: a light and transmission electron microscopy case report.Implant Dent. 2007;16(2): 195-203.
[27] Carinci F,Piattelli A,Stabellini G,et al.Calcium sulfate: Analysis of MG63 osteoblast-like cell response by means of a microarray technology.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2004;71(2):260-267.
[28] Yamauchi M,Yamaguchi T,Kaji H,et al.Involvement of calcium-sensing receptor in osteoblastic differentiation of mouse MC3T3-E1 cells.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2005; 288(3):E608-E616.
[29] Qi Y,Wang Y,Yan W,et al.Combined Mesenchymal Stem Cell Sheets and rhBMP-2-Releasing Calcium Sulfate-rhBMP-2 Scaffolds for Segmental Bone Tissue Engineering.Cell Transplant. 2012;21(4):693-705.
[30] Dasmah A,Sennerby L,Rasmusson L,et al.Intramembraneous bone tissue responses to calcium sulfate: an experimental study in the rabbit maxilla.Clin Oral Implants Res.2011;22(12): 1404-1408.
[31] Shen YX,Zhang P,Zhao JG,et al.Pedicle screw instrumentation plus augmentation vertebroplasty using calcium sulfate for thoracolumbar burst fractures without neurologic deficits.Orthop Surg.2011;3(1):1-6.
[32] Zhu X,Chen X,Chen C,et al. Evaluation of Calcium Phosphate and Calcium Sulfate Injectable Bone Cements in Sheep Vertebrae.J Spinal Disord Tech.2012;25(6): 333-337. |